Volume 10, Issue 1 (Spring 2024)
JMIS 2024, 10(1): 82-97 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: Conclusion: Spreading rumors in the workplace in organizations reduces the motivation to serve and a
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
aslani F, Heshmatzadeh A, Malekiha M. The Effect of Narcissistic Leadership on Employee Cynicism With the Mediating Role of Employee Silence and Workplace Gossip Among the Hospital Staff. JMIS 2024; 10 (1) :82-97
URL: http://jmis.hums.ac.ir/article-1-486-en.html
URL: http://jmis.hums.ac.ir/article-1-486-en.html
Department of Counseling, Faculty of Humanities, Hazrat-e Masoumeh University, Qom, Iran.
Full-Text [PDF 6227 kb]
(851 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (1710 Views)
Full-Text: (876 Views)
Introduction
Competent, committed and motivated employees are the main key to providing quality services in organizations. Organizations and managers should know that human capital is the most valuable asset of the organization. Today, one of the challenges facing organizations is pessimism. Cynicism is the tendency to consider self-interests as the main motivator and do not believe in the purity of intentions, human virtue and altruism. This negative attitude has infiltrated many organizations and is the main reason for many unfavorable and negative organizational consequences and one of the problematic issues in the organization.
Another factor is organizational silence, which refers to employees’ refusal to comment on organizational and management problems [22], and it occurs when supervisors or leaders misbehave with their coworkers [24]. Organizational silence does not only mean not speaking, but also means not writing and not listening to each other [26]. In recent years, much attention has been drawn to the dark or destructive side of leadership. The increase in repetition of destructive behaviors of leaders and the important effects of these behaviors on individual and organizational outcomes in the workplace is the most important reason for paying attention to the dark side of leadership [17].
Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the effect of narcissistic leadership style on employee cynicism with the mediating role of employee silence and workplace gossip.
Methods
This is a descriptive cross-sectional study. The study population consists of the headquarters staff of Dr. Gharazi Hospital in Isfahan, Iran (n=150). Using Cochran’s formula, the sample size was determined 108, and samples were selected by a simple random sampling method. To collect data, the narcissism scale by Hochwarter & Thompson (2012) [44, 46], the employee silence scale by Tangirala and Ramanujam (2008) [47], the organizational cynicism scale by Dean et al. (2009) [48], and the workplace gossip scale by Kuo et al. (2015) [49] were used. To analyze the data, descriptive statistics (Mean±standard deviation) and structural equation modeling (SEM) method were used in SPSS software, version 25 and SmartPLS software, version 4.
Results
Participants included 103 (95.4%) men and 5 (4.6%) women. Eight people (7.4%) had a high school diploma, 58 (53.7%) had a associate or bachelor’s degree, and 42 (38.9%) had a master’s degree or higher. Nine people (8.3%) were less than 30 years old, 39 (36.1%) aged 30-40 years, 37 (34.3%) aged 40-50 years, and 23 (21.3%) aged over 50 years. In the current research, according to the hypotheses, the model is presented in the significant mode (Figure 1) and the standard mode (Figure 2).
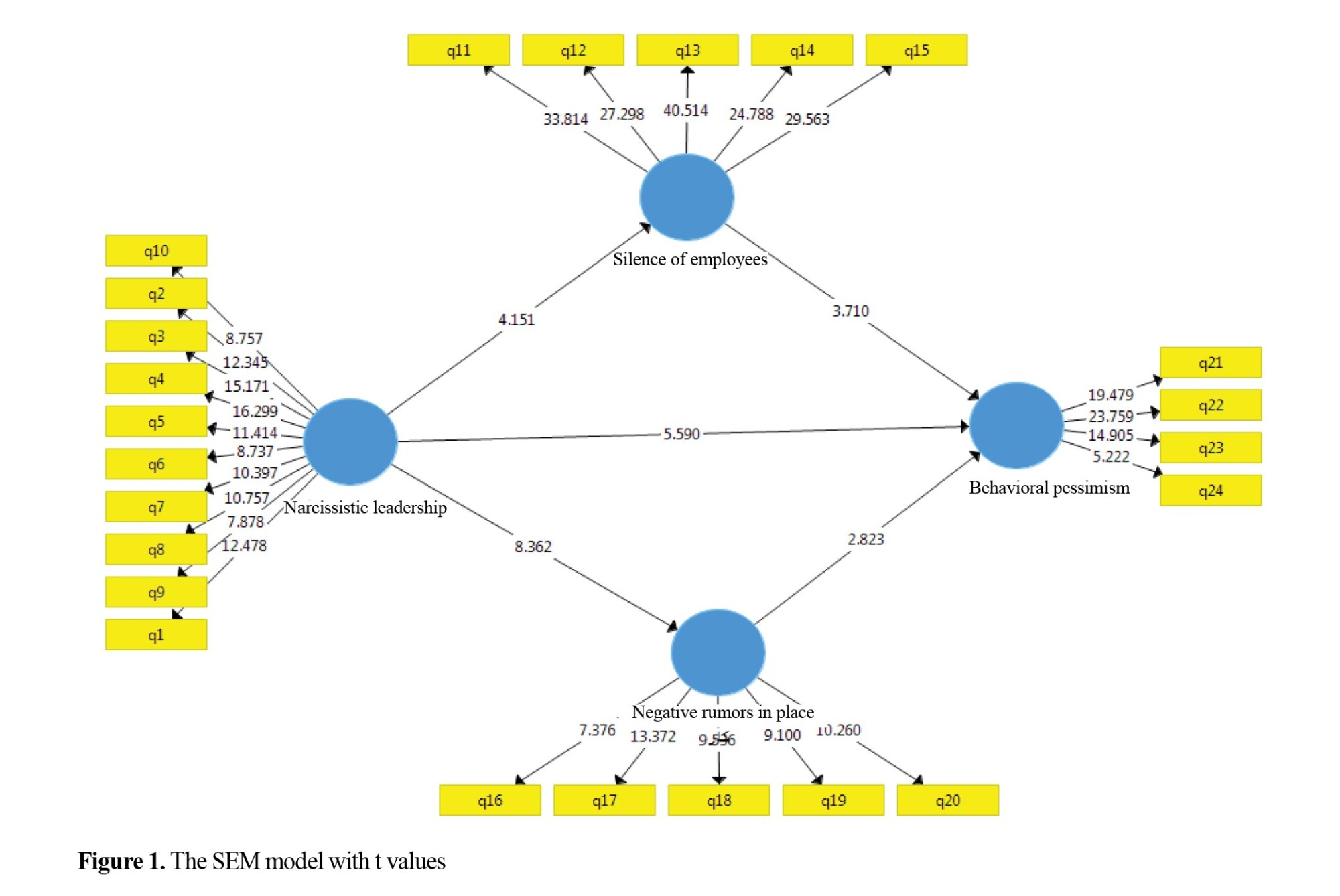
The first hypothesis in the present study was that narcissistic leadership has an effect on employee cynicism with the mediating role of employee silence. The results showed that the t value was 4.445 (outside the range [−1.96, 1.96]) and the standardized path coefficient was 0.147 (P<0.001). Therefore, the first hypothesis was confirmed.
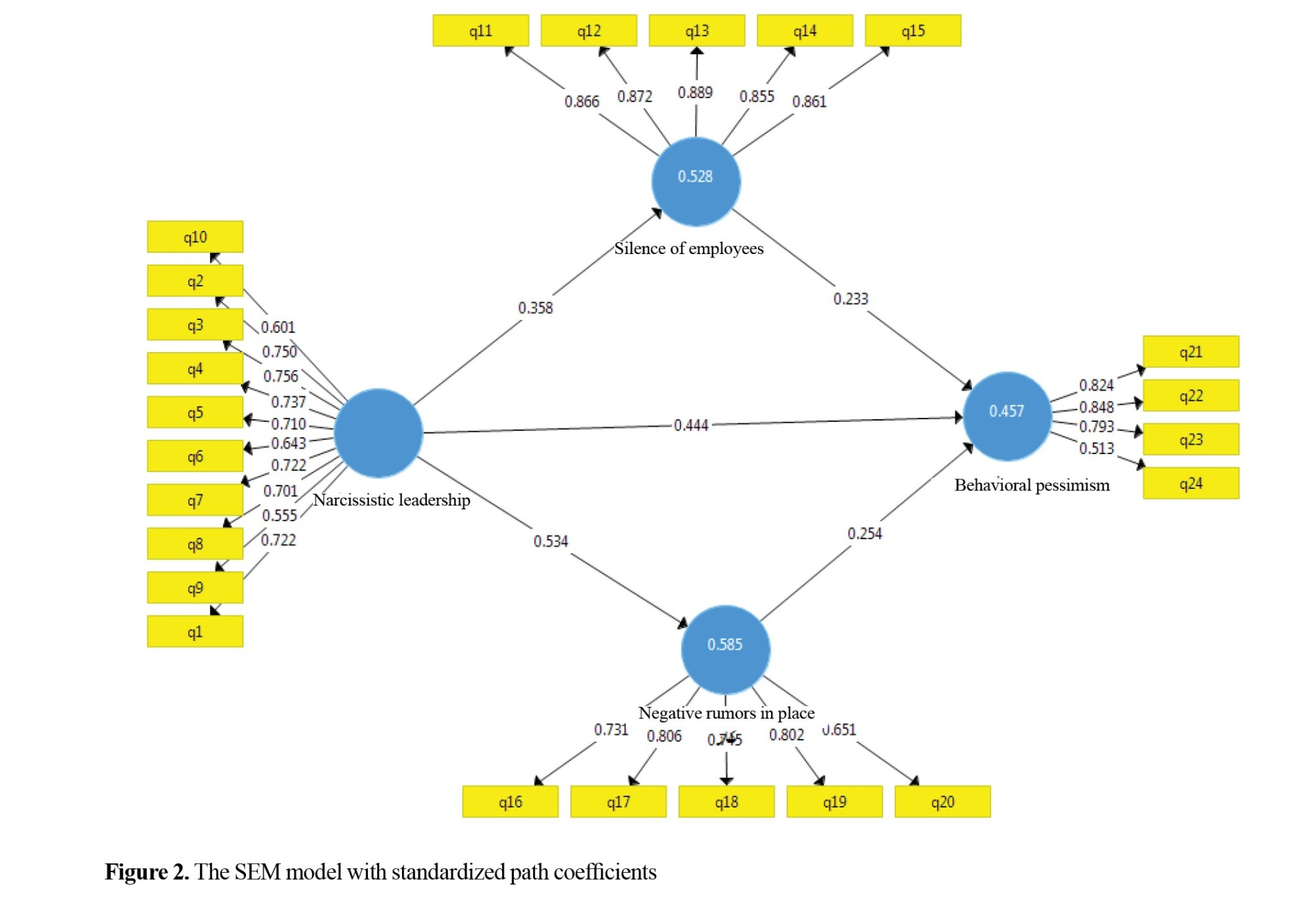
The second hypothesis was that narcissistic leadership style has an effect on employee cynicism with the mediating role of workplace gossip. The results showed that the t value was 3.950 (outside the range [−1.96, 1.96]) and the standardized path coefficient was 0.135 (P<0.001). Therefore, the second hypothesis was also confirmed.
The third hypothesis was that narcissistic leadership style has an effect on workplace gossip. The results showed that the t value was 8.362 (outside the range [−1.96, 1.96]) and the standardized path coefficient was 0.534 (P=0.001). Therefore, the third hypothesis was also confirmed.
Conclusion
The leadership style in an organization is effective on the performance of that organization. Paying attention to the leadership style is important for the quantitative and qualitative improvement of the organization. Based on the results of the present study, narcissistic leadership style in a hospital can affect employee cynicism with the mediating role of employee silence and workplace gossip. The effects of employee silence and workplace gossip on employee cynicism are also positive and significant. Therefore, it is recommended to use qualitative methods to examine the barriers to effective leadership in the hospitals in Iran, especially teaching hospitals. This study had some limitations such as the use of a self-report for collecting information and the short duration of study due to the high workload and working conditions in the hospitals.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Payame Noor University, Natanz Branch (Code: IR.REC.PNU.1401.77070).
Funding
This research did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors.
Authors' contributions
Supervision of research implementation, and Data analysis: Farshid Aslani; Research execution: Atefeh Heshmatzadeh; Writing an article and submitting an article: Farshid Aslani, Atefeh Heshmatzadeh, and Marziyeh Malekieh.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We hereby express our thanks and appreciation to the directorate, management and all the staff of Shahid Gharehi Hospital.
Competent, committed and motivated employees are the main key to providing quality services in organizations. Organizations and managers should know that human capital is the most valuable asset of the organization. Today, one of the challenges facing organizations is pessimism. Cynicism is the tendency to consider self-interests as the main motivator and do not believe in the purity of intentions, human virtue and altruism. This negative attitude has infiltrated many organizations and is the main reason for many unfavorable and negative organizational consequences and one of the problematic issues in the organization.
Another factor is organizational silence, which refers to employees’ refusal to comment on organizational and management problems [22], and it occurs when supervisors or leaders misbehave with their coworkers [24]. Organizational silence does not only mean not speaking, but also means not writing and not listening to each other [26]. In recent years, much attention has been drawn to the dark or destructive side of leadership. The increase in repetition of destructive behaviors of leaders and the important effects of these behaviors on individual and organizational outcomes in the workplace is the most important reason for paying attention to the dark side of leadership [17].
Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the effect of narcissistic leadership style on employee cynicism with the mediating role of employee silence and workplace gossip.
Methods
This is a descriptive cross-sectional study. The study population consists of the headquarters staff of Dr. Gharazi Hospital in Isfahan, Iran (n=150). Using Cochran’s formula, the sample size was determined 108, and samples were selected by a simple random sampling method. To collect data, the narcissism scale by Hochwarter & Thompson (2012) [44, 46], the employee silence scale by Tangirala and Ramanujam (2008) [47], the organizational cynicism scale by Dean et al. (2009) [48], and the workplace gossip scale by Kuo et al. (2015) [49] were used. To analyze the data, descriptive statistics (Mean±standard deviation) and structural equation modeling (SEM) method were used in SPSS software, version 25 and SmartPLS software, version 4.
Results
Participants included 103 (95.4%) men and 5 (4.6%) women. Eight people (7.4%) had a high school diploma, 58 (53.7%) had a associate or bachelor’s degree, and 42 (38.9%) had a master’s degree or higher. Nine people (8.3%) were less than 30 years old, 39 (36.1%) aged 30-40 years, 37 (34.3%) aged 40-50 years, and 23 (21.3%) aged over 50 years. In the current research, according to the hypotheses, the model is presented in the significant mode (Figure 1) and the standard mode (Figure 2).

The first hypothesis in the present study was that narcissistic leadership has an effect on employee cynicism with the mediating role of employee silence. The results showed that the t value was 4.445 (outside the range [−1.96, 1.96]) and the standardized path coefficient was 0.147 (P<0.001). Therefore, the first hypothesis was confirmed.

The second hypothesis was that narcissistic leadership style has an effect on employee cynicism with the mediating role of workplace gossip. The results showed that the t value was 3.950 (outside the range [−1.96, 1.96]) and the standardized path coefficient was 0.135 (P<0.001). Therefore, the second hypothesis was also confirmed.
The third hypothesis was that narcissistic leadership style has an effect on workplace gossip. The results showed that the t value was 8.362 (outside the range [−1.96, 1.96]) and the standardized path coefficient was 0.534 (P=0.001). Therefore, the third hypothesis was also confirmed.
Conclusion
The leadership style in an organization is effective on the performance of that organization. Paying attention to the leadership style is important for the quantitative and qualitative improvement of the organization. Based on the results of the present study, narcissistic leadership style in a hospital can affect employee cynicism with the mediating role of employee silence and workplace gossip. The effects of employee silence and workplace gossip on employee cynicism are also positive and significant. Therefore, it is recommended to use qualitative methods to examine the barriers to effective leadership in the hospitals in Iran, especially teaching hospitals. This study had some limitations such as the use of a self-report for collecting information and the short duration of study due to the high workload and working conditions in the hospitals.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Payame Noor University, Natanz Branch (Code: IR.REC.PNU.1401.77070).
Funding
This research did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors.
Authors' contributions
Supervision of research implementation, and Data analysis: Farshid Aslani; Research execution: Atefeh Heshmatzadeh; Writing an article and submitting an article: Farshid Aslani, Atefeh Heshmatzadeh, and Marziyeh Malekieh.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We hereby express our thanks and appreciation to the directorate, management and all the staff of Shahid Gharehi Hospital.
References
- Venkatraman S, Sundarraj R. Assessing organizational health-analytics readiness: Artifacts based on elaborated action design method. J Enterp Inf Manage. 2023; 36(1):123-50. [Link]
- Adamopoulos I, Frantzana A, Syrou N. Epidemiological surveillance and environmental hygiene, SARS-CoV-2 infection in the community, urban wastewater control in Cyprus, and water reuse. J Contemporary Stud Epidemiol Public Health. 2023; 4(1):ep23003. 2023. [DOI:10.29333/jconseph/12948]
- Deyhimpour M, Dolati H. [The effect of organizational transparency on organizational paranoia mediated by social capital (Persian)]. Soc CapManage. 2020; 7(3):373-98. [DOI:10.22059/JSCM.2020.305339.2026]
- Koochaki Z, Karimi S. [Relationship between covid-19 anxiety and quality of life with the mediating role of sleep quality in people with diabetes (Persian)]. J Diabetic Nurs. 2021; 9(3):1660-73. [Link]
- Kramer RM. 1. Organizational paranoia: Origins and dynamics. Res Organ Behav. 2001; 23:1-42. [DOI:10.1016/S0191-3085(01)23002-0]
- Kazemi Moghadasy N, Zabihi M, Shekari GA. [The relationship between organizational justice and organizational paranoia with moderating role of perceived organizational support (Persian)]. Transform Manag J. 2016; 7(14):155-80. [DOI:10.22067/pmt.v7i14.46015]
- Subramanian K. Organizational Paranoia and the Consequent dysfunction. Int J Comb Res Dev. 2017; 6(12):7121-34. [Link]
- Ihionkhan D, Itua OP. Organizational paranoia and employee performance: A case of Nigerian bottling company and seven up bottling company, Benin plants, Nigeria. Int J Humanit Soc Sci. 2018; 8(11):101-10. [DOI:10.30845/ijhss.v8n11p12]
- Monyei FE, Ezinwa PN, Emejulu GA, Moneme PC. The interplay between organizational paranoia and the productivity of deposit money banks. Int J Dev Res. 2020; 10(02):33944-9. [Link]
- Susa AM. Humor type, organizational climate, and outcomes: The shortest distance between an organization’s environment and the bottom line is laughter [PhD dissertation]. Lincoln: The University of Nebraska-Lincoln; 2002. [Link]
- Moein M, Adib Hajbaghery M. [Comparison of occupational stress among female nurses and female members of the medical group in chosen training hospitals in Isfahan (Persian)]. Iran J Psychiatric Nurs. 2015; 3(2):1-10 . [Link]
- Hezomi H, Nadrian H. What determines psychological well-being among Iranian female adolescents? Perceived stress may overshadow all determinants. Health Promot Perspect. 2018; 8(1):79-87. [DOI:10.15171%2Fhpp.2018.10] [PMID]
- Ferreira N. Enhancing career wellbeing: The role of workplace friendship, career adaptability and organisational commitment. In: Potgieter I, Ferreira N, Coetzee M, editors. Theory, research and dynamics of career wellbeing. Cham: Springer; 2019. [DOI:10.1007/978-3-030-28180-9_10]
- Rani H, Shah SMM, Umrani WA, Syed J, Afshan G. Employee state paranoia: Linking abusive supervision with employee voice behavior. Leadersh Organ Dev J. 2021; 42(7):1053-70. [Link]
- Bagheri G, Zarei R, Aeen MN. Organizational silence (basic concepts and its development factors). Ideal Type Manag 2012; 1(1):47-58. [Link]
- Henriksen K, Dayton E. Organizational silence and hidden threats to patient safety. Health Serv Res. 2006; 41(4 Pt 2):1539-54. [DOI:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00564.x] [PMID]
- Zehir C, Erdogan E. The association between organizational silence and ethical leadership through employee performance. Procedia Soc Behav Sci. 2011; 24:1389-404. [DOI:10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.09.054]
- Dankoski ME, Bickel J, Gusic ME. Discussing the undiscussable with the powerful: Why and how faculty must learn to counteract organizational silence. Acad Med. 2014; 89(12):1610-3. [DOI:10.1097/ACM.0000000000000428] [PMID]
- Güçlü N. The relation of leadership styles with organizational silence and organizational learning. Int Online J Educ Sci. 2017; 9(1). [Link]
- Bordia P, Kiazad K, Restubog SLD, DiFonzo N, Stenson N, Tang RL. Rumor as revenge in the workplace. Group Organ Manag. 2014; 39(4):363-88. [DOI:10.1177/1059601114540750]
- Huo LA, Huang P, Fang X. An interplay model for authorities’ actions and rumor spreading in emergency event. Phys Stat Mech Appl. 2011; 390(20):3267-74. [DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2011.05.008]
- Doaei HA, Eslami G, Gholami M. [Investigating the impact of organizational rumor and gossip on employees’ job attitudes and performance through organizational cynicism in the public sector (Persin)]. Transform Manag J. 2021; 13(1):55-84. [Link]
- Abdi H, Sobhani A, Mousavian SM, Abbasi H. [The Impact of organizational bullying on organizational cynicism through organizational silence and impression management (case study: Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch) (Persian)]. Res Educ Leadersh Manag. 2018; 4(16):37-70. [DOI:10.22054/jrlat.2019.46646.1483]
- Rayisi A, Nastiezaie N. [The relationship between organizational cynicism and organizational anti-citizenship behavior with the mediating role of organizational envy (Persian)]. Career Organ Couns. 2019; 11(38):117-36. [DOI:10.29252/jcoc.11.1.117]
- Ebrahimi A, Bagheri Gara Bollagh H, Eynali M, Baki Hashemi MM. [The role of organizational trauma on silence and organizational cynicism in a health service provider center (Persian)]. Neurosci J Shefaye Khatam. 2019; 7(3):51-60. [DOI:10.29252/shefa.7.3.51]
- Gheadamini Harouni A, Ebrahimzadeh Dastjerdi R, Ebrahimpour AR. [Investigating the effect of bullying in the workplace on deviant behaviors in the workplace through Toxic leadership and destructive leadership (Case study: Islamic Azad University of Isfahan (Khorasgan) (Persian)]. Soc Stud. 2022; 15(54):35-59. [Link]
- Maamari BE, Majdalani JF. Emotional intelligence, leadership style and organizational climate. Int J Organ Anal. 2017; 25(2):327-45. [DOI:10.1108/IJOA-04-2016-1010]
- Dele AO, Nanle M, Abimbola OS. Impact of leadership style on organizational climate in the Nigerian insurance industry. Int J Bus Industr Mark. 2015; 1(3):45-52. [Link]
- Asrar-ul-Haq M, Anjum T. Impact of narcissistic leadership on employee work outcomes in banking sector of Pakistan. Future Bus J. 2020; 6:34. [Link]
- Arar K, Oplatka I. Narcissistic leadership. In: Arar K, Oplatka I, editors. Advanced theories of educational leadership. Policy implications of research in education, vol 14. Cham: Springer; 2022. [DOI:10.1007/978-3-031-14510-0_8]
- Alipour A, Ghadami A, Alipour Z, Abdollahzadeh H. [Preliminary validation of the Corona Disease Anxiety Scale (CDAS) in the Iranian sample (Persian)]. Health Psychol. 2020; 8(32):163-75. [DOI:10.30473/hpj.2020.52023.4756]
- Wu YL, Shao B, Newman A, Schwarz G. Crisis leadership: A review and future research agenda. Leadersh Q. 2021; 32(6):101518. [DOI:10.1016/j.leaqua.2021.101518]
- DiFonzo N, Bordia P. Rumor in organizational contexts. In: Hantula DA, editor. Advances in social and organizational psychology. London: Psychology Press; 2006. p. 261-86. [DOI:10.4324/9781410617446-20]
- DiFonzo N, Bordia P. Rumor psychology: Social and organizational approaches. Washington: American Psychological Association; 2007. [DOI:10.1037/11503-000]
- Alsudias L, Rayson P. COVID-19 and Arabic Twitter: How can Arab world governments and public health organizations learn from social media? Paper presented at: NLP COVID-19 Workshop: An emergency workshop at ACL 2020. Association for Computational Linguistics. [Link]
- Lee Marks M. Consulting in mergers and acquisitions: Interventions spawned by recent trends. J Organ Change Managt. 1997; 10(3):267-79. [Link]
- Gholipor A, Khanifar H, Fakheri Koozeh kanan S. [Effects of manager’s narcissism on organizational disturbance (Persian)]. Organ Cult Manag. 2009; 6(18):79-93. [Link]
- Faizi T, kheirandish M, Latifi S. [Individual, organizational and managerial antecedents and consequences of managers narcissism: Using document analysis and Shannon Entropy (Persian)]. J Organ Behav Stud Q. 2019; 30(2):171-88. [Link]
- Wilkerson JM, Evans WR, Davis WD. A test of coworkers’ influence on organizational cynicism, badmouthing, and organizational citizenship behavior. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2008; 38(9):2273-92. [DOI:10.1111/j.1559-1816.2008.00391.x]
- Moghadam A, Mahmoudi Meymand M. [The effect of organizational cynicism on tendency to deviant behaviours; the moderating role leadership style (Persian)]. Manag Stud Dev Evol. 2018; 27(89):73-89. [DOI:10.22054/jmsd.2018.26185.2479]
- Prewitt JE, Weil R, McClure AQ. Crisis leadership-an organizational opportunity. Aust J Bus Manag Res. 2015; 4(12):60-74. [DOI:10.52283/NSWRCA.AJBMR.20110106A07]
- DuBrin AJ. Handbook of research on crisis leadership in organizations. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar; 2013. [Link]
- Aboramadan M, Turkmenoglu MA, Dahleez KA, Cicek B. Narcissistic leadership and behavioral cynicism in the hotel industry: The role of employee silence and negative workplace gossiping. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2020; 33(2):428-47. [Link]
- Hochwarter WA, Thompson KW. Mirror, mirror on my boss’s wall: Engaged enactment’s moderating role on the relationship between perceived narcissistic supervision and work outcomes. Hum Relat. 2012; 65(3):335-66. [DOI:10.1177/0018726711430003]
- Cowie H, Naylor P, Rivers I, Smith PK, Pereira B. Measuring workplace bullying. Aggress Violent Behav. 2002; 7(1):33-51. [DOI:10.1016/S1359-1789(00)00034-3]
- Bakhoda V, Mirzaeipour J, Khadem A. [The effect of narcissistic leadership on employees’ behavioral pessimism with the mediating role of organizational silence and spreading rumors in the workplac (Persian)].Paper presented at: 9th International Conference on Interdisciplinary Researches in Management Accounting Economics and in Iran. 19 February 2023; Tehran, Iran. [Link]
- Tangirala S, Ramanujam R. Employee silence on critical work issues: The cross level effects of procedural justice climate. Pers Psychol. 2008; 61(1):37-68. [DOI:10.1111/j.1744-6570.2008.00105.x]
- Malekiha M. [Developing a native model of work-family enrichment and survey the effect of career counseling based on the model on the facilitation of work-family and family-work conflict in Isfahan University workers (Persian)] [PhD dissertation]. Isfahan: Isfahan University; 2014. [Link]
- Eidi Pour K, Yosefy B, Zardoshtian S, Eydi, H. [Effect of toxic leadership style on organizational cynicism and job alienation of staff in the Sports and Youth Ministry of Iran with a mediating role of Machiavellianism (Persian)]. Sport Manag Stud. 2020; 12(59):135-52. [DOI:10.22089/smrj.2018.5378.2060]
Type of Study: Research |
Subject:
Special
Received: 2023/09/11 | Accepted: 2024/01/9 | Published: 2024/04/1
Received: 2023/09/11 | Accepted: 2024/01/9 | Published: 2024/04/1
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |








 hums.ac.ir
hums.ac.ir