Volume 9, Issue 1 (Spring 2023)
JMIS 2023, 9(1): 56-69 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Sagheb Ray Shirazi M, Fanaei H, Mouseli A, Madadi S, Hafezi H. Prevalence of Addiction to Video Games and its Effects Among Paramedical Students of Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences. JMIS 2023; 9 (1) :56-69
URL: http://jmis.hums.ac.ir/article-1-360-en.html
URL: http://jmis.hums.ac.ir/article-1-360-en.html
Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran.
Full-Text [PDF 1829 kb]
(1079 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (1636 Views)
Full-Text: (1898 Views)
Introduction
Video games are a type of modern technology that has become popular among people in recent years. Despite their entertainment function and positive aspects such as developing talents, increasing intelligence, expanding worldview, strengthening artistic taste, and teaching complicated concepts, their excessive use has complications such as psychological health problems (anxiety, depression, excessive daydreaming, mood changes), study and work problems, eye and muscle diseases including back pain and neck pain, and change in lifestyle, nutrition and sleep patterns [16, 17, 18]. These disorders can be diagnosed when a person is not able to control himself over playing games and does not pay attention to the priority of performing daily tasks or pursuing other interests. The tendency of people to play video games is not only affected by the content of the games, but also by individual characteristics such as personality traits. Addiction to video games occurs more in people with high agreeableness. Since paramedical students are a group of medical staff who have important clinical responsibilities, the present study aims to investigate the prevalence of video game addiction among paramedical students of Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences in Iran.
Methods
In this descriptive-analytical study with a cross-sectional design, 120 male/female students of Faculties of Health and Nursing in Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences (entrance year of 2020) participated, who had completed at least one academic semester and were willing to participate in the study. The used questionnaire included demographic information (age, sex, educational level, and major) and video game addiction survey (age of starting video games, game genre, level of academic progress, behavior, effect of video games on physical/ mental health, and the level of addiction) which was designed according to the questionnaire of Deng et al. [21]. The internal consistency of the questionnaire was determined after its completion by 30 participants (α=0.86). Its test-retest reliability was also confirmed (r=0.81). Questionnaires were distributed among students in the classroom. Data analysis was done in SPSS software, version 19 using Chi-square test and Pearson correlation test. The significance level was set at 0.05.
Results
In this study, 67.2% of the students were female and 32.8% were male. Their mean grade point average was 16.24. The data showed that 42.4% of students spent less than half an hour, 22.3% spent half an hour and 35.3% spent more than one hour on video games. Moreover, 47% of the students started playing video games at the age of 5-10, 32% at the age of 10-15, 17% at the age of 15-20, and 4% over the age of 20.
Discussion
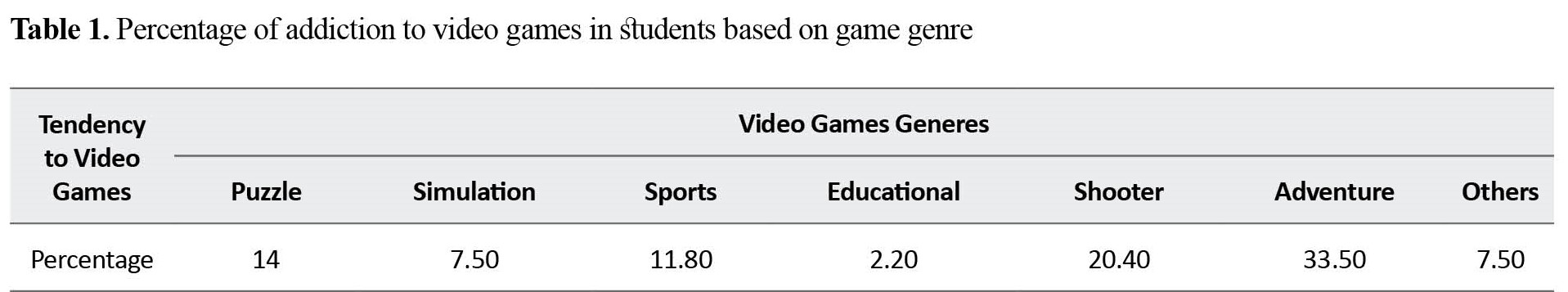
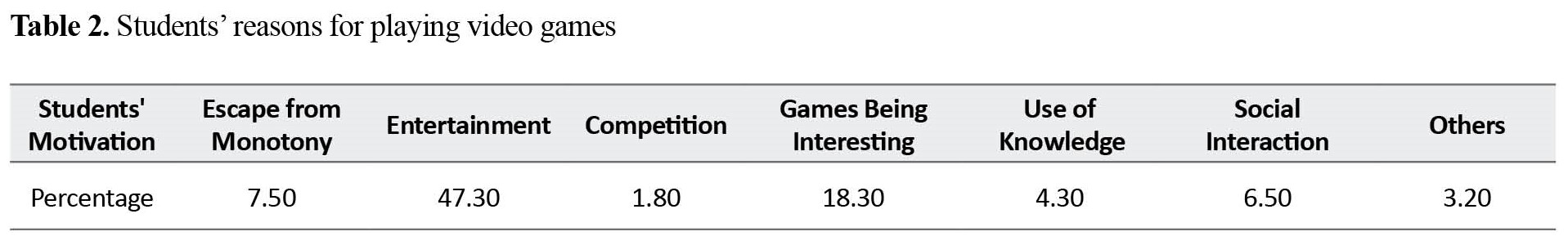
The results of this study showed a significant positive relationship between the gender of students in Hormozgan and their addiction to video games, such that the addiction was higher among male students. Most of the students had a tendency towards playing adventure (Table 1), shooter and puzzle games and they often mentioned the interesting, diverse and up-to-dateness of games as criteria for playing video games (Table 2).
There was a relationship between addiction to video games and students’
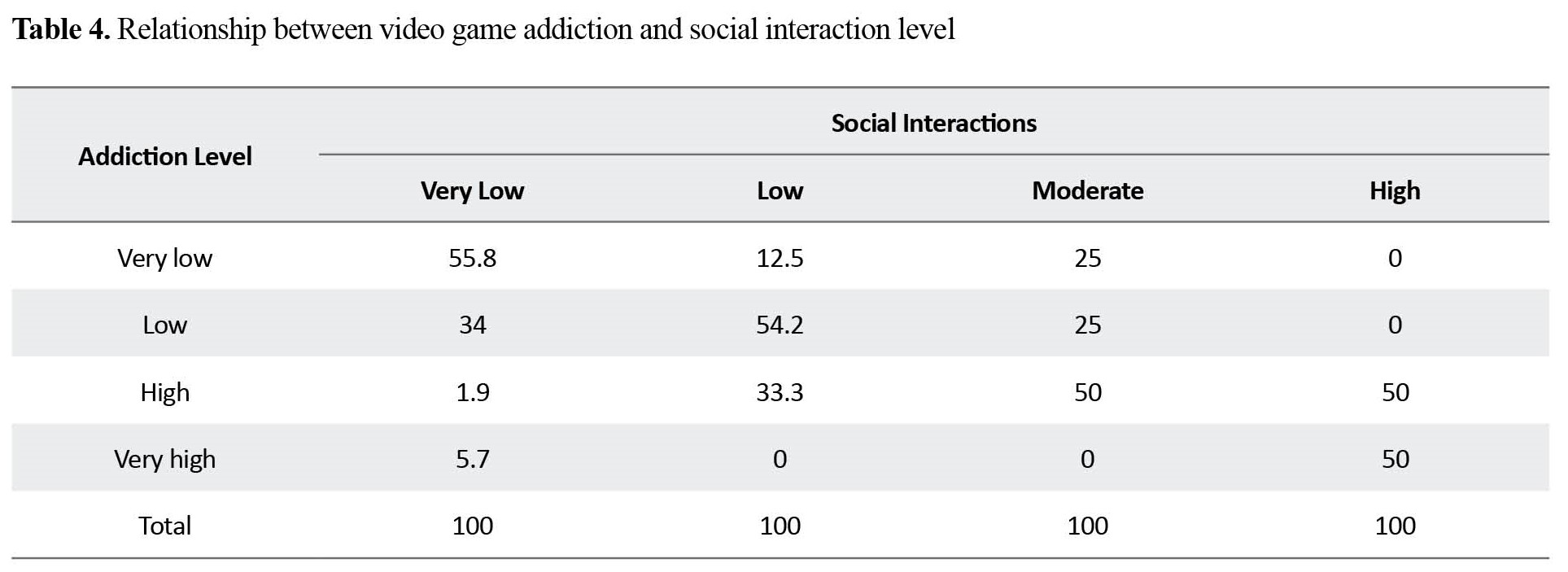
aggression/violence (Table 3), social interaction level (Table 4), and everyday task (Table 5) performance.
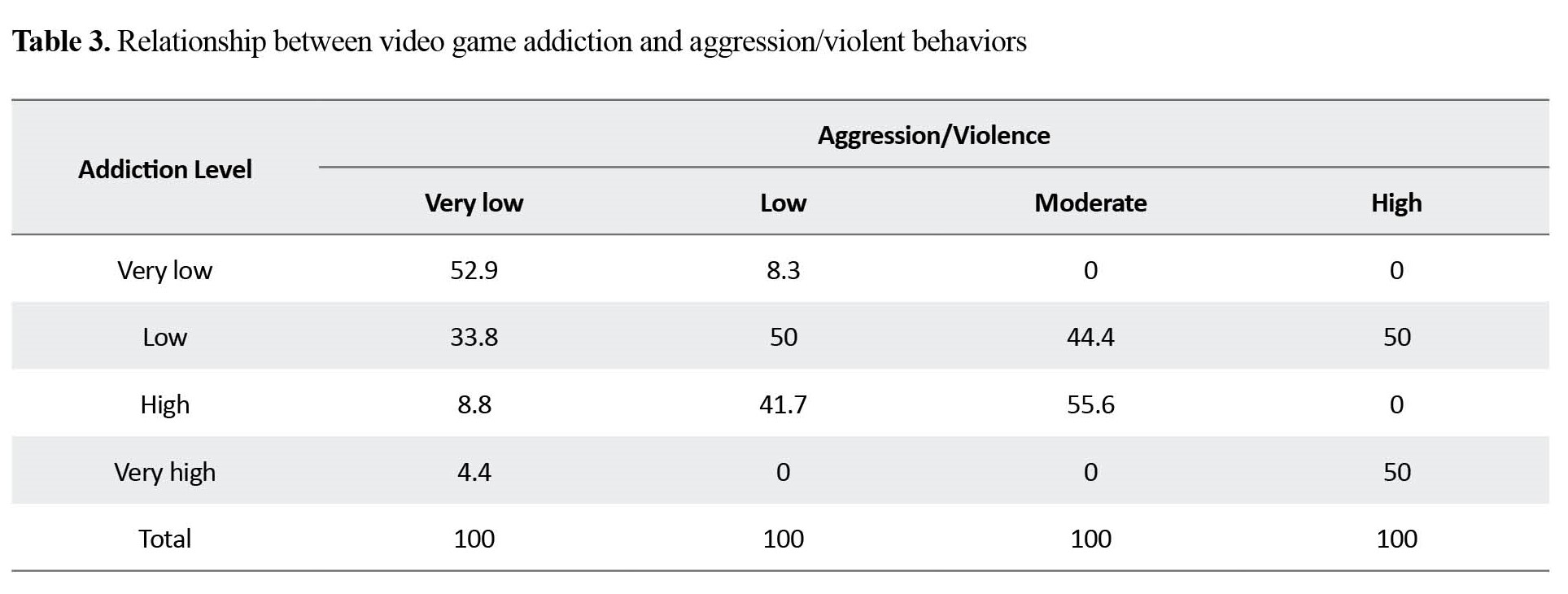
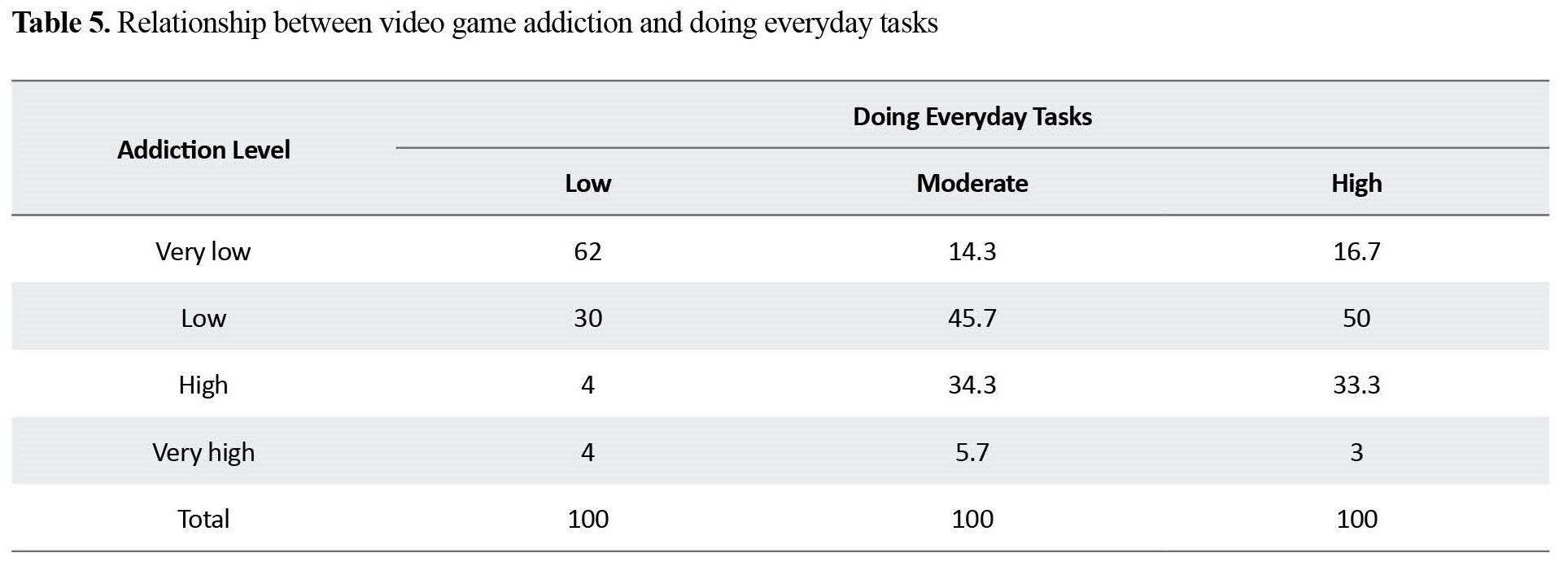
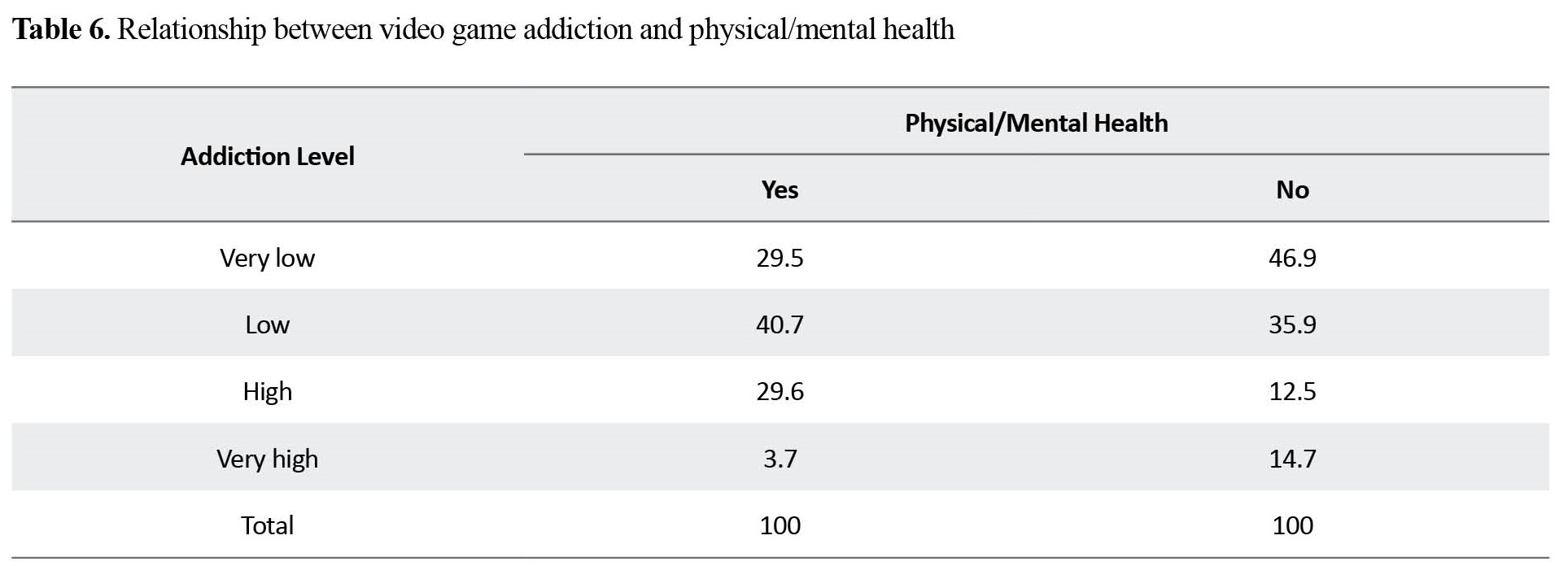
Addiction to video games increased the occurrence of aggressive and violent behaviors among students. There was no relationship between addiction to video games and physical/mental health of students (Table 6).
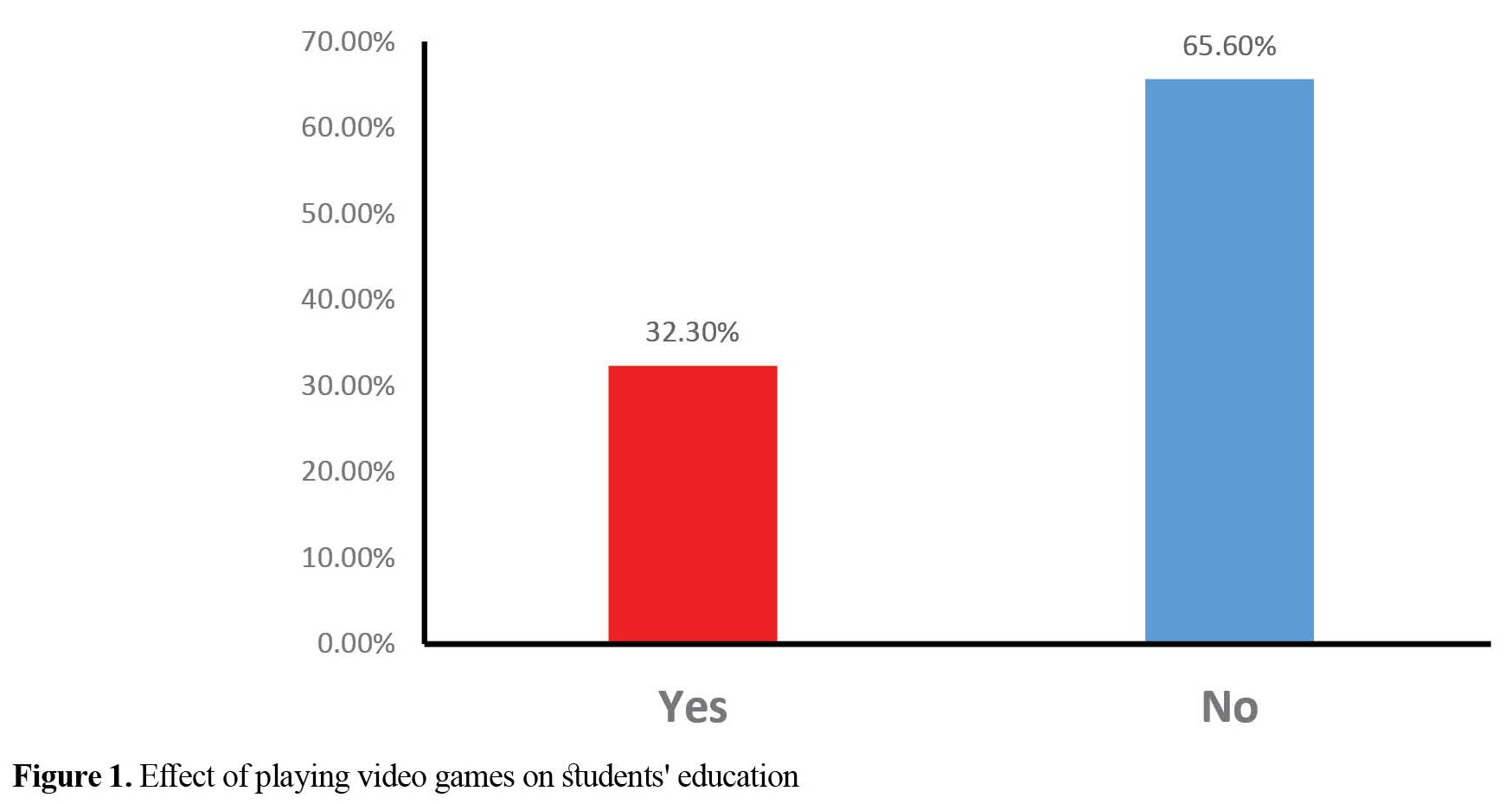
In this study, 32.3% of students’ addiction to video games had an effect on their education (Figure 1).
Video games are a type of modern technology that has become popular among people in recent years. Despite their entertainment function and positive aspects such as developing talents, increasing intelligence, expanding worldview, strengthening artistic taste, and teaching complicated concepts, their excessive use has complications such as psychological health problems (anxiety, depression, excessive daydreaming, mood changes), study and work problems, eye and muscle diseases including back pain and neck pain, and change in lifestyle, nutrition and sleep patterns [16, 17, 18]. These disorders can be diagnosed when a person is not able to control himself over playing games and does not pay attention to the priority of performing daily tasks or pursuing other interests. The tendency of people to play video games is not only affected by the content of the games, but also by individual characteristics such as personality traits. Addiction to video games occurs more in people with high agreeableness. Since paramedical students are a group of medical staff who have important clinical responsibilities, the present study aims to investigate the prevalence of video game addiction among paramedical students of Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences in Iran.
Methods
In this descriptive-analytical study with a cross-sectional design, 120 male/female students of Faculties of Health and Nursing in Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences (entrance year of 2020) participated, who had completed at least one academic semester and were willing to participate in the study. The used questionnaire included demographic information (age, sex, educational level, and major) and video game addiction survey (age of starting video games, game genre, level of academic progress, behavior, effect of video games on physical/ mental health, and the level of addiction) which was designed according to the questionnaire of Deng et al. [21]. The internal consistency of the questionnaire was determined after its completion by 30 participants (α=0.86). Its test-retest reliability was also confirmed (r=0.81). Questionnaires were distributed among students in the classroom. Data analysis was done in SPSS software, version 19 using Chi-square test and Pearson correlation test. The significance level was set at 0.05.
Results
In this study, 67.2% of the students were female and 32.8% were male. Their mean grade point average was 16.24. The data showed that 42.4% of students spent less than half an hour, 22.3% spent half an hour and 35.3% spent more than one hour on video games. Moreover, 47% of the students started playing video games at the age of 5-10, 32% at the age of 10-15, 17% at the age of 15-20, and 4% over the age of 20.
Discussion
The results of this study showed a significant positive relationship between the gender of students in Hormozgan and their addiction to video games, such that the addiction was higher among male students. Most of the students had a tendency towards playing adventure (Table 1), shooter and puzzle games and they often mentioned the interesting, diverse and up-to-dateness of games as criteria for playing video games (Table 2).


There was a relationship between addiction to video games and students’
aggression/violence (Table 3), social interaction level (Table 4), and everyday task (Table 5) performance.



Addiction to video games increased the occurrence of aggressive and violent behaviors among students. There was no relationship between addiction to video games and physical/mental health of students (Table 6).

In this study, 32.3% of students’ addiction to video games had an effect on their education (Figure 1).
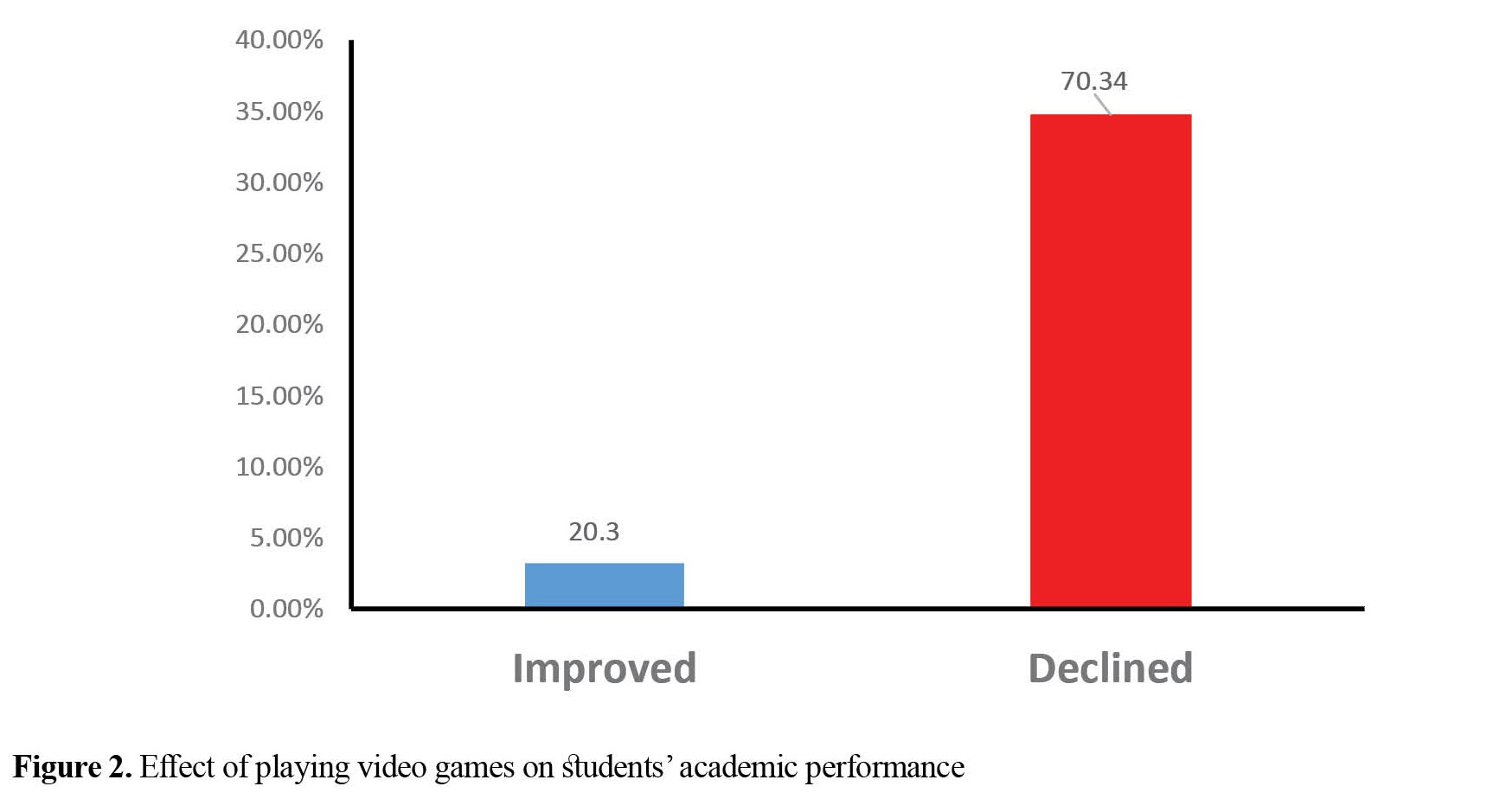
70.34% of students reported the video game addiction to be a cause of academic failure, while these games caused academic progress in 3.2% of students (Figure 2).
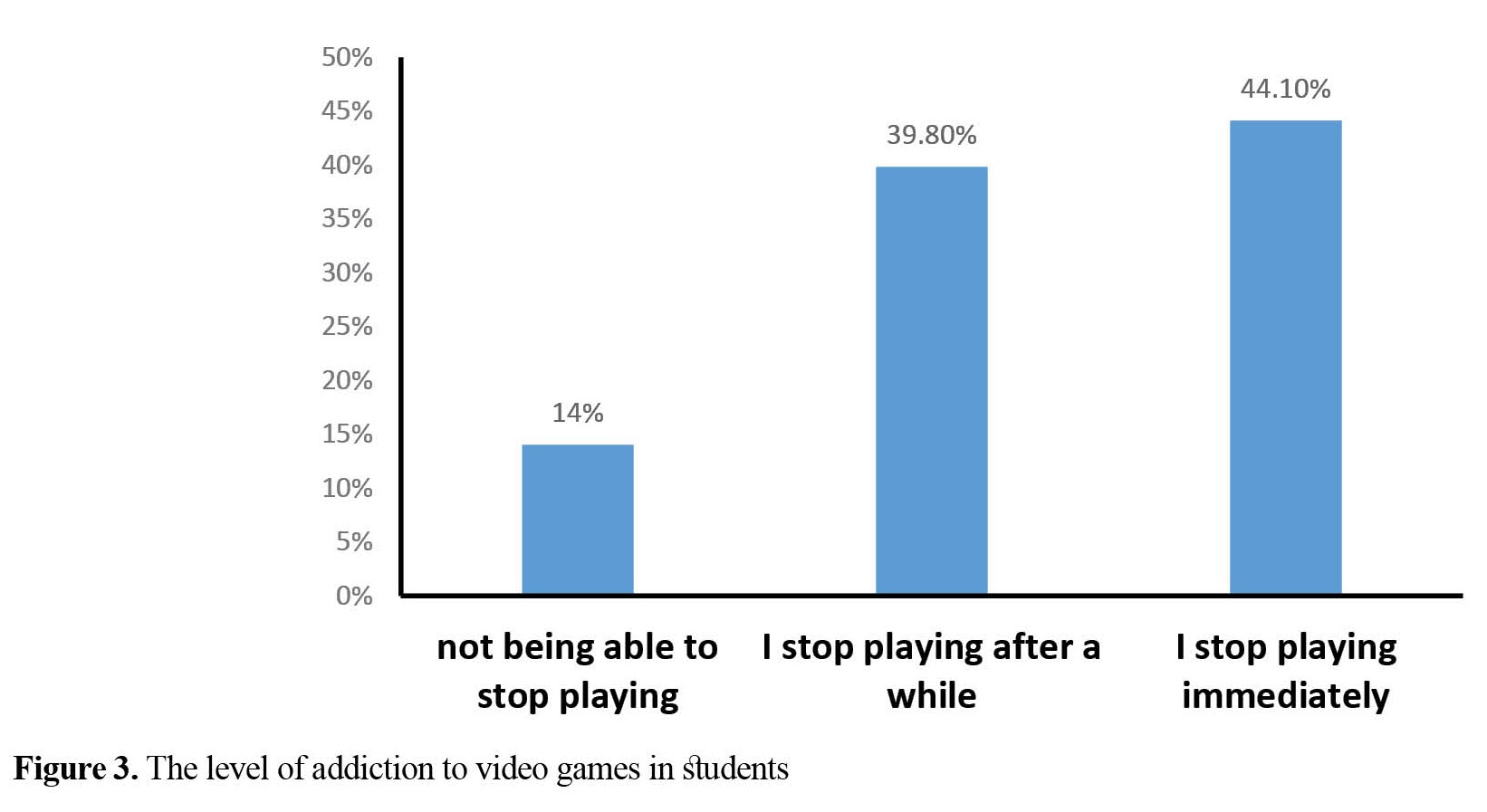
There was no significant relationship video game addiction and academic failure (Figure 3).
According to the results and the popularity of video games, especially among students, it is necessary for university officials to plan and use such games in a suitable educational environment.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study has an ethical approval from Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences (Code: IR.MUI.IR.HUMS.REC.1399.390)
Funding
This study was supported by Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences.
Authors' contributions
Conceptualization, project administration, writing: Malihe Sagheb Ray Shirazi; data analysis, writing, and editing: Hafseh Fanaei; supervision: Ali Mouseli; Data collection: Soheila Madadi and Hossein Hafezi.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the students participated in this study for their cooperation.
References
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study has an ethical approval from Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences (Code: IR.MUI.IR.HUMS.REC.1399.390)
Funding
This study was supported by Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences.
Authors' contributions
Conceptualization, project administration, writing: Malihe Sagheb Ray Shirazi; data analysis, writing, and editing: Hafseh Fanaei; supervision: Ali Mouseli; Data collection: Soheila Madadi and Hossein Hafezi.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the students participated in this study for their cooperation.
References
- Spring D. Gaming history: Computer and video games as historical scholarship. Rethinking Hist. 2015; 19(2):207-21. [DOI:10.1080/13642529.2014.973714]
- Seraji F, AliBakhshi M. [Parents’ worries about harm caused to adolescents by computer games: Findings from a mixed methods research (Persian)]. Q J Fam Res. 2015; 12(1):31-50. [Link]
- Harris J. The effects of computer games on young children: A review of the research. London: Home Office, Research, Development and Statistics Directorate; 2001. [Link]
- Shirani Bidabadi E, Behyan S, Hashemianfar S. [The role of computer games subculture in antisocial behaviors of high school teenagers in Isfahan in 2016 (Persian)]. J Cul Commun Stud. 2018; 18(40):185-223. [DOI:10.22083/jccs.2018.97971.2254]
- Lister M. Gamification: The effect on student motivation and performance at the post-secondary level. Issues Trends Educ Technol. 2015; 3(2):1-22. [DOI:10.2458/azu_itet_v3i2_lister]
- Adachi PJ, Willoughby T. Do video games promote positive youth development? J Adolesc Res. 2013; 28(2):155-65. [DOI:10.1177/0743558412464522]
- Horne-Moyer HL, Moyer BH, Messer DC, Messer ES. The use of electronic games in therapy: A review with clinical implications. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2014; 16(12):520. [DOI:10.1007/s11920-014-0520-6] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Masoudnia E, Pourrahimian E. [Impact of computer game on incidence of behavioral disorders among male elementary school students (Persian)]. J Appl Soc. 2016; 27(3):117-34. [DOI:10.22108/jas.2016.20501]
- Saffarian Hamedani S, Abdollahi M, Daeizade H, Bayat Y. [The relationship between the amount of playing computer games and students’ mental health and academic performance (Persian)]. Inform Commun Technol Educ Sci. 2013; 3(11):5-20. [Link]
- Huard Pelletier V, Lessard A, Piché F, Tétreau C, Descarreaux M. Video games and their associations with physical health: A scoping review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2020; 6(1):e000832. [DOI:10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000832] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Farmanbar R, Tavana Z, Eatebsary F, Atr Karroshan Z. [The relationship between playing computer games with Aggression among middle school students in the city of Rasht in 2013 (Persian]. Iran J Health Educ Health Promot. 2013; 1(3):57-66. [Link]
- Ng BD, Wiemer-Hastings P. Addiction to the internet and online gaming. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2005; 8(2):110-3. [DOI:10.1089/cpb.2005.8.110] [PMID]
- Maramis JR, Maengkom KS. [Relationship levels of online game addiction with levels of physical activity in high school students (Indonesian)]. Klabat J Nur. 2022; 4(1):81-9. [DOI:10.37771/kjn.v4i1.801]
- Abdollahi R, Rasoulizadeh TK. The effect of computer games on personality traits and adolescent adjustment. Police Woman. 2013; 7(18): 84-106. [Link]
- Kamenar Čokor D, Bernik A. The impact of computer games on preschool children’s cognitive skills. In: Arai K, editor. Intelligent computing. lecture notes in networks and systems. 2021; Cham: Springer International Publishing. [DOI:10.1007/978-3-030-80129-8_37]
- Ebrahimi S, Khammarnia M, Porvazn N, Karamipur M, Jamshidzahi H, Setoodezadeh F, et al. [The prevalence of internet addiction and its relationship with quality of sleep and quality of life among students of Zahedan University of Medical Sciences (Persian)]. J Sch Public Health Inst Public Health Res. 2018; 16(2):126-37. [Link]
- Abdollahzadeh R, Mehranpour R. [Studying the level of addiction to Internet among Internet centers’ users of Birjand County in 2016 (Persian)]. J Prev Med. 2016; 3(3):8-13. [Link]
- Deimazar G, Kahouei M, Forouzan M, Skandari F. [Effects of online social networks on sleep quality, depression rate, and academic performance of high school students (Persian)]. Koomesh. 2019; 21(2):312-7. [Link]
- Mohamadbeigi A, Ghazavi A, Mohammad salehi N, Ghamari F, Saeidi A. [Effect of internet addiction on educational status of Arak University of Medical Sciences students, spring 2009 (Persian)]. J Arak Uni Med Sci. 2010; 12(4):95-102. [Link]
- Buneviciene I, Bunevicius A. Prevalence of internet addiction in healthcare professionals: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2021; 67(5):483-91. [DOI:10.1177/0020764020959093] [PMID]
- Deng YX, Hu M, Hu GQ, Wang LS, Sun ZQ. [An investigation on the prevalence of internet addiction disorder in middle school students of Hunan province (Chinese)]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2007; 28(5):445-8. [PMID]
- Shokouhi-Moqhaddam S, Khezri-Moghadam N, Javanmard Z, Sarmadi-Ansar H, Aminaee M, Shokouhi-Moqhaddam M, et al. A study of the correlation between computer games and adolescent behavioral problems. Addict Health. 2013; 5(1-2):43-50. [PMID] [PMCID]
- Anderson CA, Gentile DA. Violent video game effects on aggressive thoughts, feelings, physiology, and behavior. In: DA Gentile, editor. Media violence and children: A complete guide for parents and professionals. Westport: Praeger Publishers; 2014. [Link]
- Dirandeh E, Sohrabi MR, Dirandeh A, Kaghazloo L, Hajihashemi Z, Pouriran R. The effect of video games on teenagers’ behavior and performance: A cross-sectional study in Tehran. Soc Determ Health. 2015; 1(3):120-7. [DOI:10.22037/sdh.v1i3.12094]
Type of Study: Research |
Subject:
General
Received: 2021/10/19 | Accepted: 2022/12/6 | Published: 2023/05/31
Received: 2021/10/19 | Accepted: 2022/12/6 | Published: 2023/05/31
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |








 hums.ac.ir
hums.ac.ir